CBD 101: Getting the Facts on CBD
When it comes to the exploding cannabis industry, it is hard to go anywhere without hearing the word CBD. What once was a taboo topic is now being touted as beneficial and rapidly making its way into commercial stores and online retailers all over the country, and all over the world. So in order to better prepare you to understand the unfamiliar jargon of the cannabis world, the team at CBD Doctor has prepared this helpful glossary and basic guide to help you get acquainted with some of the often-complicated terms in the industry.
So, whether this is just the beginning of your CBD journey or you want to take it to the next level, we have taken some time to break down the basic verbiage of CBD, the latest player in the wellness industry.
Here is our basic guide to get you started, but if you have any more questions about CBD or any of our products, feel free to visit our FAQs page or Beginner's Guide to CBD, which both feature helpful information to guide you along the way.
CBD 101 Glossary
Bioavailability:
When deciding which form of CBD is best for you, this becomes an important item to consider. Bioavailability means the degree and rate absorbed into the bloodstream, a.k.a how quickly and how much CBD is processed by your body so that you feel it take effect. Smoking and vaping are more immediate than others, because the CBD goes directly into your lungs and system. Sublingual absorption using a tincture or oil – letting the oil sit under your tongue until it is absorbed by the capillaries – has a different bioavailability than ingesting edibles or capsules; for example, your response time can be lengthened by how much food you’ve eaten. For prescription medications, your doctor has already factored bioavailability into the ratio when determining the prescribed dosage.
Broad spectrum:
Newer to the CBD game than its full spectrum and isolate teammates, broad spectrum CBD is produced when the extracted substance maintains all of the benefits of full spectrum CBD – including plant compounds and terpenes – but with all trace amounts of THC removed. Studies show that broad spectrum CBD offers more varied benefits than CBD isolate, containing all of the natural elements and cannabinoids of the plant. If you’re looking to add CBD to your wellness regimen while avoiding any interaction with THC – or strict THC laws in your state – you’ll find that broad spectrum is the ideal solution. Broad spectrum CBD provides you with a worry-free solution to enjoying the naturally soothing benefits of CBD oils.
Cannabinoids:
When you hear any companies or products use the term cannabinoid – bear in mind, CBD is itself a cannabinoid – it refers to substances extracted from the cannabis plant including both the psychoactive and non-psychoactive compounds known as THC and CBD, as well as additional compounds called terpenes. Other known cannabinoids that are picking up in popularity are CBN, THCV, THCA, and CBG. Cannabinoids interact with the Endocannabinoid System to bind directly or indirectly to ECS receptors, which behave like chemical messengers to turn on or turn off signaling in the body. Cannabinoids serve different purposes and can be created inside the body (endocannabinoids), in plants (phytocannabinoids), or synthetically in the laboratory (synthetic cannabinoids). CBD is an example of a phytocannabinoid.
CBD (Cannabidiol):
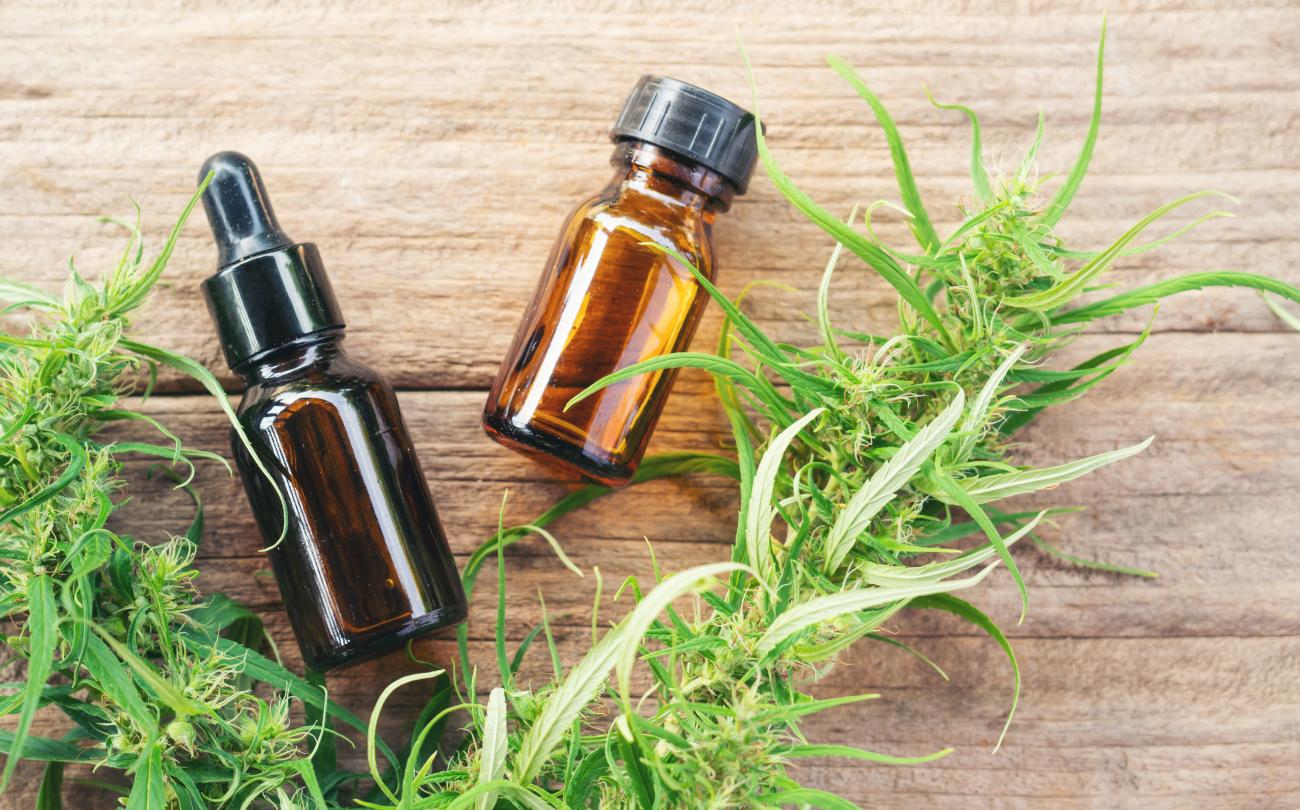
One of over 100 identified cannabinoids, CBD has been said to have analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties, among other emerging research on the subject. Unlike THC, CBD is not psychoactive, as even in its full spectrum form, it only contains trace elements of less than 0.3 percent THC. This quality makes CBD an appealing option for those who are looking for relief from pain and other symptoms without the mind-altering effects of marijuana or other pharmaceutical drugs. CBD is offered in a range of different kinds of products, including oils, tinctures, vapes, capsules, edibles, flowers, topicals, skin care, bath & body, and even pet care.
CBD isolate:
The purest form of CBD, isolate is ideal as it is tasteless and odorless, making it an adaptable ingredient that can be used to create a variety of homemade CBD products. If you prefer a more basic form of CBD without all the bells and whistles, CBD isolate might be your best option, as it contains only CBD without any of the other compounds, trace amounts of THC, or terpenes. Many believe that because of this, CBD isolate does not provide all of the beneficial properties found in full and broad spectrum.
Endocannabinoid System (ECS):
More commonly referred to as ECS, the Endocannabinoid System is a complex system in the human body, which maintains all processes throughout the brain and body, including how the body manages appetite, pain, sleep, pleasure, and mood. The purpose of this system is that of creating balance within the body to achieve the optimal state for maintaining health and natural wellness. CBD and other cannabinoids work with the ECS to better regulate body functions.
Entourage Effect:
When companies promise their product will yield an entourage effect, they mean the total result of the symbiosis, or working together, of the compounds found in the cannabis plant— cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids — which interact in harmony to produce more enhanced effects from the plant than would exist without all elements present. This is why some prefer products made from full or broad spectrum CBD rather than pure CBD isolate.
Extraction:
While the name seems to be self-explanatory, it never hurts to be sure, so here goes. When relating to CBD, the term extraction refers to the removal process of CBD from the plant flowers. This is done in order to blend the oil into convenient products like tinctures and topicals. Some extraction processes require solvents or additives, while others do not.
Full spectrum:
As its name suggests, full spectrum CBD contains the full range and beneficial properties of all cannabinoids and beneficial terpenes from its source plant, with less than 0.3 percent THC. Full spectrum is associated with the entourage effect in that it offers the complete benefits of all of the cannabinoids and terpenes present from the source plant. This is often considered the most effective type of CBD.
Hemp:
A jack of all trades, hemp refers to the strain of the cannabis sativa plant and its fibers, originally used to make fabrics and other useful textiles, construction materials, and CBD-rich oil with low traces of THC. Hemp is now bred with higher amounts of CBD and is legal in more states than marijuana. CBD derived from hemp and marijuana is identical. Our CBD, if available in full spectrum, can contain trace amounts of THC with less than 0.3 percent, but these particular products do not contain enough THC to produce psychoactive effects.
Psychoactive:
Many labels will warn about products having psychoactive effects, particularly when dealing with substance with mind-altering properties. This is most often used to describe the intoxicating effects associated with THC. While our full spectrum products do contain trace amounts of THC (less than 0.3 percent), this is below the legal limit and too small an amount to produce any psychoactive effects.
Sublingual:
To break this term down, we can look at its literal roots meaning “under the tongue,” which is precisely how this method is delivered, by taking a dose of CBD and holding it underneath the tongue for about 60 seconds. This is anecdotally the amount of time needed for the capillaries to more quickly absorb the CBD. Sublingual delivery allows greater bioavailability of active substances and faster absorption of CBD than edibles.
Terpenes:
Organic compounds that occur naturally in plants, terpenes serve a host of roles, including determining a plant’s scent and flavor. You might be more familiar with their presence as essential oils released by the sticky resin glands of plants, herbs, and fruits to create aromas of, let’s say, pine or citrus. The creation of terpene profiles has helped determine the effects associated with particular products or strains, which may change in the presence of other compounds, a.k.a. the entourage effect. Terpenes may come to serve larger roles in aiding in relaxation or acting as anti-inflammatory agents. Consider the calming effects of lavender essential oils, which works because of the presence of a terpene called linalool, also a naturally occurring terpene in cannabis.
THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol):
The most well-known, or shall we say notorious, of over 100 identified cannabinoids, THC has been known for its analgesic and mind-altering qualities, most notably affecting a user’s focus, pleasure, and perception of time. Substances and products containing THC can cause psychoactive effects, but CBD as a whole contains little to no THC. Broad spectrum and CBD isolate are both THC-free, while full spectrum CBD contains less than 0.3 percent THC, which is below the legal limit and too small an amount to produce any psychoactive effects.
We hope that these terms give you a solid foundation from which to explore the CBD industry with a little more know-how. If you have further questions about CBD or our products, feel free to consult our Ask A Doctor section, where our board-certified doctors can provide more answers.
Our CBD Doctor blog features additional articles to guide your CBD journey, including features on “Which CBD Products Are Right for Me?” and “What Can CBD Do for Your Skin?”